Fluoridation In Pediatric Dentistry
Fluoridation in Pediatric Dentistry
Pediatric dentistry is a specialized field focused on the oral health of children from infancy through adolescence. Here are some of the key services provided in pediatric dentistry and how they address decay in children:
Preventive Services:
- Regular Check-ups: Routine dental visits help monitor oral health and catch any issues early.
- Dental Cleanings: Professional cleanings remove plaque and tartar buildup, reducing the risk of decay.
- Fluoride Treatments: Application of fluoride helps strengthen tooth enamel and prevent cavities.
- Dental Sealants: These thin coatings are applied to the chewing surfaces of molars to protect against decay.
Treatment of Decay
- Fillings: If decay is present, the dentist removes the affected area and fills the cavity with a suitable material like composite resin.
- Pulp Therapy: For advanced decay that reaches the inner pulp of the tooth, treatments like pulpotomy or pulpectomy might be necessary.
- Crowns: Severe decay may require crowns (caps) to cover and protect extensively damaged teeth.
- Extractions: In extreme cases where decay has extensively damaged a tooth, extraction might be necessary.
Orthodontic Evaluations
Dentists assess the need for orthodontic treatment and refer children to orthodontists if required.
Educational Guidance:
Dentists educate children and parents on proper oral hygiene practices, including brushing, flossing, and diet choices.
Behavioral Guidance
Pediatric dentists are trained to handle children's behavioral challenges, making dental visits a positive experience.

Decay in children, often known as dental caries or cavities, can occur due to various factors:
- Poor Oral Hygiene: Inadequate brushing, flossing, and rinsing.
- Diet: Excessive consumption of sugary or acidic foods and drinks.
- Bacteria: The presence of bacteria in the mouth that interact with food particles and produce acids that erode tooth enamel.
- Lack of Fluoride: Insufficient exposure to fluoride, which helps in remineralizing and strengthening teeth.
Pediatric dental care focuses on early intervention and preventive measures to combat decay. Regular check-ups, coupled with education about proper oral hygiene and diet, are crucial in maintaining children’s oral health. The goal is to instill good habits early and address any issues promptly to ensure a lifetime of healthy smiles.
Fluoride treatments are a common preventive measure in pediatric dentistry, especially for young dental patients. Fluoride is a mineral that helps prevent tooth decay by making teeth more resistant to acid attacks from plaque bacteria and sugars in the mouth. Here are some key points about fluoride treatments in young dental patients:
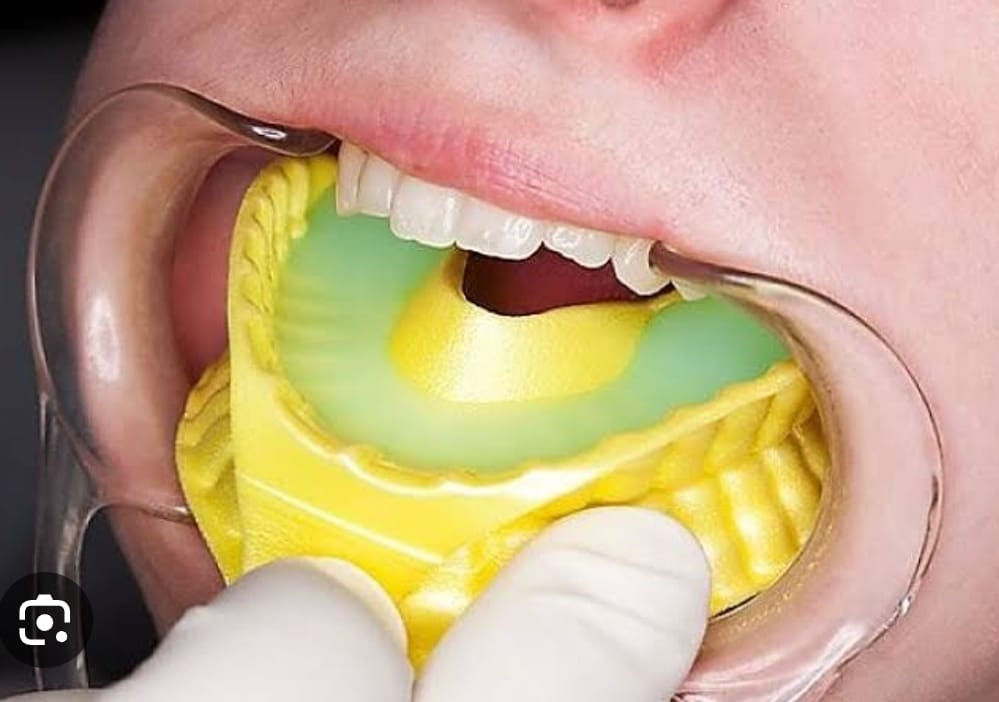
Strengthens Tooth Enamel:
Fluoride treatments, usually applied as a gel, foam, or varnish, help strengthen the enamel—the outer layer of teeth. This makes teeth more resistant to decay caused by acids produced by bacteria and acidic foods.
Reverses Early Decay
In cases of early-stage decay or demineralization (white spots on teeth indicating initial decay), fluoride treatments can potentially reverse this process by remineralizing the enamel and stopping the decay from progressing.
Application Methods
Fluoride can be applied in various ways:
• Topical Application: Dentists apply fluoride directly to the teeth using gels, foams, varnishes, or rinses during dental visits.
• Systemic Fluoride: This refers to fluoride that children get from sources like fluoridated water, supplements, or fluoride-containing toothpaste.
Frequency of Treatment
The frequency of fluoride treatments may vary depending on a child's risk of developing cavities, their oral hygiene habits, and their exposure to other sources of fluoride.
Professional Guidance
Pediatric dentists evaluate a child's risk of tooth decay and determine the appropriate frequency and type of fluoride treatment. They may recommend treatments every 3, 6, or 12 months.
Safety Measures:
Fluoride treatments are safe when used as directed. However, excessive fluoride intake can lead to a condition called fluorosis, which affects tooth enamel. Dentists ensure that the right amount of fluoride is applied based on a child's age and risk factors.
Combined with Oral Hygiene
Fluoride treatments work best when combined with good oral hygiene practices, such as regular brushing with fluoride toothpaste and a balanced diet low in sugary and acidic foods and drinks.
Fluoride treatments are an essential part of preventive dental care for children. They provide an extra layer of protection against cavities and support the overall oral health of young dental patients. Consulting with a pediatric dentist helps determine the most suitable fluoride regimen based on a child’s individual needs.
The procedure for fluoride application in children involves several steps and can vary based on the type of fluoride product used. Here’s a general outline of the process:
1. Dental Examination:
Before applying fluoride, we conduct a thorough dental examination to assess the child’s oral health and determine the need for fluoride treatment.
2. Cleaning Teeth:
We clean the child’s teeth to remove any plaque or debris, ensuring that the fluoride can be applied to clean tooth surfaces.
3. Selecting Fluoride Product:
Depending on the child’s age, risk of cavities, and specific dental needs, the pediatric dentist at Shah Dental Specialists may choose a fluoride gel, foam, varnish, or rinse for application.
4. Application:
Fluoride Gel or Foam: If using a gel or foam, the dentist or hygienist may place a small amount of the fluoride product into a tray or use a brush to apply it directly to the teeth. The child is instructed to bite down on the tray or keep their mouth open for a short period to allow the fluoride to adhere to the teeth. The excess is then suctioned or rinsed out after a specified time.
5. Fluoride Varnish:
For fluoride varnish, the dentist or hygienist uses a small brush to apply the varnish to the surfaces of the teeth. The varnish dries quickly, forming a protective coating on the enamel. The child is instructed to avoid eating or drinking for a short period to allow the varnish to set.
6. Post-Application Instructions:
After the fluoride application, the child might be advised not to eat, drink, or rinse for about 30 minutes to maximize the fluoride’s effectiveness.
7. Follow-up and Recommendations:
The dentist may recommend a specific frequency for fluoride treatments based on the child’s oral health needs and risk of cavities. They might also provide guidance on proper oral hygiene practices, including brushing with fluoride toothpaste and maintaining a balanced diet.
It’s essential for parents or caregivers to follow the dentist’s instructions regarding fluoride application and any post-treatment care to ensure its effectiveness in preventing tooth decay in children. Additionally, regular dental check-ups and consultations with a pediatric dentist help monitor the child’s oral health and adjust fluoride treatments as needed.
Pedodontia / dentistry for children :
This specialty deals with the diseases of teeth and gums of children, right from birth through adolescence till the age of 14 years. Early detection of dental caries (tooth decay), identification and correction of aberrant habits like thumb sucking, tongue thrusting and bite corrections all are entailed under this specialty.
Treatments rendered are:
RCT of milk teeth (Pulpectomy)
Tooth fluoridation / gel/ varnish application
Rampant caries / caries in multiple teeth
Nursing bottle caries
Habit breaking appliances
Space maintainers
Braces for children
Tooth fillings
Treatment of knocked out teeth or fractured teeth
Need an Emergency Help?
Call Us!
Testimonials
What people say about Us.

Mr. and Mrs.Bagla
They are dentists with good skill and talent…soft spoken and well behaved..

Vipin Netriwal
I was dealing with a dental surgical complication from my previous dentist since last 3-4 months for which I consulted so many doctors. A friend of mine suggested me to consult Dr. Gaurav Shah and after getting the treated by Dr. Gaurav Shah, my problem vanished in 15 days. It is also pertinent to mention here that both the husband and wife (Dr. Gaurav Shah and Dr. Veena Gauri Shah) are very kind hearted, very soft spoken and behave with patient in such a manner that the patient feels relieved of pain. Thanks a lot.

Arun Chordia
My experiences with Dr. Shah have always been extremely pleasant. His professional approach along with top quality service delivery ensures all round dental care.

